Our eyes provide valuable insight into our overall health. In fact, many systemic health issues can make their presence known through changes in the eyes. One such condition is diabetes, which can affect not only the body’s organs but also the health of our eyes. A diabetic eye exam is a specialized check-up that helps assess your eye health, looking for signs of damage caused by diabetes.
How Diabetes Affects Your Eyes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts how the body manages insulin, a hormone crucial for converting sugar into energy. When the body doesn’t use insulin effectively or doesn’t produce enough, sugar builds up in the bloodstream, which can lead to a variety of complications, including those affecting the eyes.
Types of Diabetes & Their Impact on Eye Health
There are two primary types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Often diagnosed in childhood, this form of diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Typically developing in adulthood, Type 2 diabetes happens when the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, causing blood sugar levels to rise.
Potential Eye Conditions Linked to Diabetes
If left untreated or if poorly managed, diabetes can lead to several serious eye conditions, such as:
Diabetic Retinopathy: Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to leakage, bleeding, or blockages. New, fragile blood vessels may also form, increasing the risk of vision loss.
Retinal Detachments: Scar tissue from abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina can cause the retina to detach from the back of the eye. If not treated quickly, this can result in permanent vision loss.
Diabetic Macular Edema: Occurs when fluid leaks from damaged blood vessels into the macula, causing it to swell and impairing central vision. This condition can make it difficult to see sharp, detailed images.
Glaucoma: People with diabetes are nearly twice as likely to develop glaucoma, a condition where pressure inside the eye increases, potentially damaging the optic nerve. This can occur when new blood vessels grow on the iris and block the flow of fluid from the eye.
Recognizing Symptoms Early
Although managing diabetes effectively can help reduce your likelihood of developing these conditions, it doesn’t eliminate the risk entirely. It’s important to watch for symptoms like:
- Blurry or fluctuating vision
- Seeing flashes of light or floaters
- Sudden or gradual vision loss
- Eye pain or increased pressure
These symptoms may indicate that something is wrong with your eyes, so it’s crucial to consult your optometrist. However, keep in mind that many eye conditions related to diabetes can develop silently, without noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. This is why regular diabetic eye exams are essential for early detection and timely intervention.
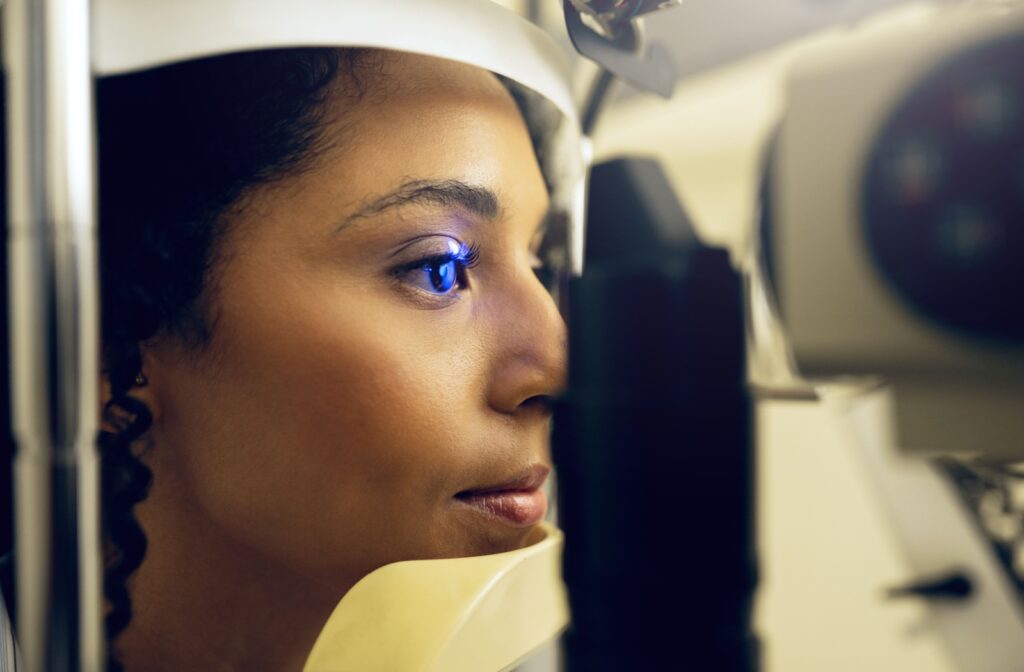
What to Expect During a Diabetic Eye Exam
A diabetic eye exam is a comprehensive check-up designed to detect early signs of damage caused by diabetes. The process involves pupil dilation, allowing your optometrist to thoroughly examine the internal structures of your eyes and spot potential issues.
Key Steps in the Diabetic Eye Exam
1. Initial Measurements
The exam begins with measuring the pressure inside your eyes using a tonometry instrument. This helps assess the risk of glaucoma, which is more common in people with diabetes.
2. Visual Field Test
Next, a visual field test may be conducted to check your peripheral vision. You’ll be asked to focus on a central point while lights flash in different areas of your vision. This helps detect any areas where vision might be compromised.
3. Pupil Dilation
Special eye drops are used to dilate your pupils, which takes about 20 to 30 minutes. This allows for a more detailed examination of the retina and other internal structures. While your vision may become blurry and light sensitivity may increase during this time, these effects are temporary. It’s a good idea to bring someone along to drive and wear sunglasses to help with discomfort.
4. Advanced Imaging
Once your pupils are dilated, your optometrist will use imaging techniques like Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and retinal photography to capture detailed scans of your retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. This helps identify any early signs of diabetic damage.
5. Slit Lamp Examination
Using a slit lamp and ophthalmoscope, your optometrist will closely examine the health of your eye, looking for any signs of diabetic retinopathy or other conditions.
6. Discussion & Follow-Up
After completing the exam, your optometrist will go over the results with you and recommend any necessary follow-up treatments or care. This is an important opportunity to ask questions and ensure you’re on the right path to maintaining healthy vision.
Why Diabetic Eye Exams Are Important
Regular eye exams are a critical part of managing diabetes. They allow your optometrist to track any changes in your eye health over time, identify problems early, and prevent severe complications that could lead to vision loss. By detecting diabetic-related eye conditions in their early stages, treatment can be started promptly, reducing the risk of long-term damage.
Fortunately, in Alberta, some of the cost of diabetic eye exams is covered under the provincial healthcare plan.
Schedule Your Diabetic Eye Exam Today
Diabetes can significantly impact your eye health, but regular diabetic eye exams can help protect your vision. If you have diabetes, don’t wait for symptoms to appear—schedule your exam today. Visit Calgary Family Eye Doctors to ensure your eyes stay healthy and your vision remains clear.